Agentic commerce is an approach to online shopping where AI agents autonomously perform tasks on behalf of customers, including product discovery, price comparison, and purchase completion, with minimal human intervention.
This represents a fundamental shift from traditional e-commerce. Instead of customers browsing websites and making decisions themselves, AI systems handle these responsibilities.
If you run a Shopify store, this affects how customers will find and buy your products. This guide explains what agentic commerce means in practical terms and what steps you should consider.
Agentic Commerce Definition
Agentic commerce refers to e-commerce transactions where intelligent AI agents act autonomously on behalf of users. These agents can search across multiple platforms, analyze product specifications, compare prices, handle logistics, and complete purchases without requiring step-by-step human direction.
The term combines “agentic,” meaning capable of taking independent action, with “commerce.” Unlike traditional automation that follows predetermined rules, agentic systems pursue goals and adapt their approach based on circumstances.
Example: A customer tells their AI assistant, “Find running shoes under $150 with good arch support and have them delivered by Friday.” The AI agent searches multiple retailers, compares options based on reviews and specifications, selects the best match, and completes the purchase, all without the customer visiting any websites.

Agentic Commerce vs Standard AI Personalization
Standard AI personalization reacts to customer data. It analyzes past purchases and browsing history, then provides recommendations. The customer still makes all decisions and completes all actions.
Agentic commerce takes this further. AI agents don’t just recommend products; they take action. They can adjust content, trigger workflows, optimize checkout flows, and complete transactions independently.
| Feature | Standard AI Personalization | Agentic Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-making | Customer decides | AI decides within parameters |
| Action capability | Recommendations only | Full transaction execution |
| Autonomy level | Reactive | Proactive and goal-oriented |
| Human involvement | Required at every step | Minimal oversight |
The shift is from “what products should we show this customer” to “what should the AI do next to achieve the customer’s goal.”
AI Agents vs Chatbots
This question comes up frequently, and the distinction matters.
Chatbots respond to questions based on fixed scripts or keyword matching. When customers ask something outside the script, chatbots typically fail or escalate to human support. They answer queries but don’t take independent action.
AI agents act. They can trigger workflows, access backend systems, make decisions based on business rules, and execute multi-step processes. They remember past interactions and adapt their responses accordingly.
Example comparison:
- Chatbot: Customer asks “Where is my order?” Chatbot retrieves tracking information and displays it.
- AI Agent: Customer asks “Where is my order?” Agent retrieves tracking, notices the package is delayed, proactively reaches out with updated delivery estimate, offers a discount code for the inconvenience, and flags the carrier issue for internal review.
The agent didn’t just answer a question. It identified a problem, took corrective action, and improved the customer experience without being asked.
Importance of Agentic Commerce
Three developments in early 2026 moved this from theoretical to practical.
The Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP)
On January 11, 2026, Shopify and Google released the Universal Commerce Protocol. UCP is a standardized system that allows any AI assistant to interact with any participating merchant.
Before UCP, each AI system needed custom integration with each store. Now, AI assistants from OpenAI (ChatGPT), Google (Gemini), Microsoft (Copilot), and others can query product catalogs, check inventory, and complete purchases through a single protocol.
Major retailers including Walmart and Target joined at launch. Payment processors Visa and Stripe are integrated. For Shopify merchants, UCP support is built into the platform by default.
Improved AI Capabilities
The underlying language models reached a capability threshold where they can reliably handle complex shopping scenarios. Earlier versions made too many errors for practical commercial use. Current models understand context, maintain conversation history, and make fewer obvious mistakes.
Platform Integration
Shopify’s Winter 2026 Edition added several agentic features:
- Sidekick now executes actions rather than just answering questions
- Agentic Storefronts allow AI assistants to browse and purchase from your store
- Built-in UCP support makes stores discoverable to AI agents automatically
Merchants don’t need to build custom integrations. The infrastructure exists.
AI Agent Architecture
AI agents operate in a continuous cycle. Understanding this helps explain what they can and cannot do.
The Agent Loop:
- Perception: The agent gathers data from available sources, including store inventory, customer history, market trends, and external signals.
- Reasoning: The agent processes information through a large language model. This is where analysis and decision-making occur.
- Planning: The agent breaks goals into specific steps. For a purchase, this might include: search products, filter by criteria, compare options, verify availability, apply discounts, process payment.
- Action: The agent executes planned steps through APIs and integrations.
- Learning: The agent evaluates results and adjusts future behavior. Did the recommendation match customer preferences? Was the delivery estimate accurate?
This cycle runs continuously, not just when triggered by human input. Unlike rule-based automation, agents adapt their approach when circumstances change.

Best Use Cases for Agentic Commerce
Based on current implementations, certain use cases show clear results.
Inventory Management
AI agents can predict demand by analyzing sales patterns, seasonal trends, competitor actions, and external factors like weather. They maintain optimal stock levels without manual intervention.
Typical results: 20-40% reduction in stockouts, 15-25% decrease in overstock situations.
Dynamic Pricing
Agents adjust prices based on demand, competitor pricing, margin requirements, and inventory levels. They operate within parameters you set.
Note: This requires careful implementation. Frequent price changes can erode customer trust. Most merchants limit adjustment frequency and magnitude.
Customer Service
AI agents handle routine inquiries: order status, return requests, product questions, sizing guidance. They resolve straightforward issues and escalate complex ones.
Typical results: 40-60% reduction in support ticket volume, with maintained or improved satisfaction scores.
Personalized Marketing
Agents create individualized campaigns based on actual customer behavior rather than broad segments. Timing, content, and channel selection are optimized per customer.
Areas Requiring Caution
- Brand messaging: AI can draft content, but brand voice requires human oversight
- High-value decisions: Large orders or strategic choices need human review
- Limited data situations: New products or stores lack sufficient history for reliable AI predictions
- Compliance matters: Legal and regulatory decisions should not be fully automated
Shopify Sidekick in Practice
Shopify Sidekick demonstrates how agentic features work in a merchant context.
Before agentic features: Creating a promotional campaign required multiple steps. Open the discount section, configure parameters, create customer segment, build email template, set up automation triggers, test, and launch.
With Sidekick: You can say: “Create a 20% discount for first-time customers this weekend and set up a welcome email campaign.”
Sidekick creates the discount code with correct conditions, builds an appropriate customer segment, drafts the email, configures automation timing, and presents everything for your approval.
You still review and approve. But the execution work transfers to the AI, freeing time for decisions that require your judgment.
Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP)
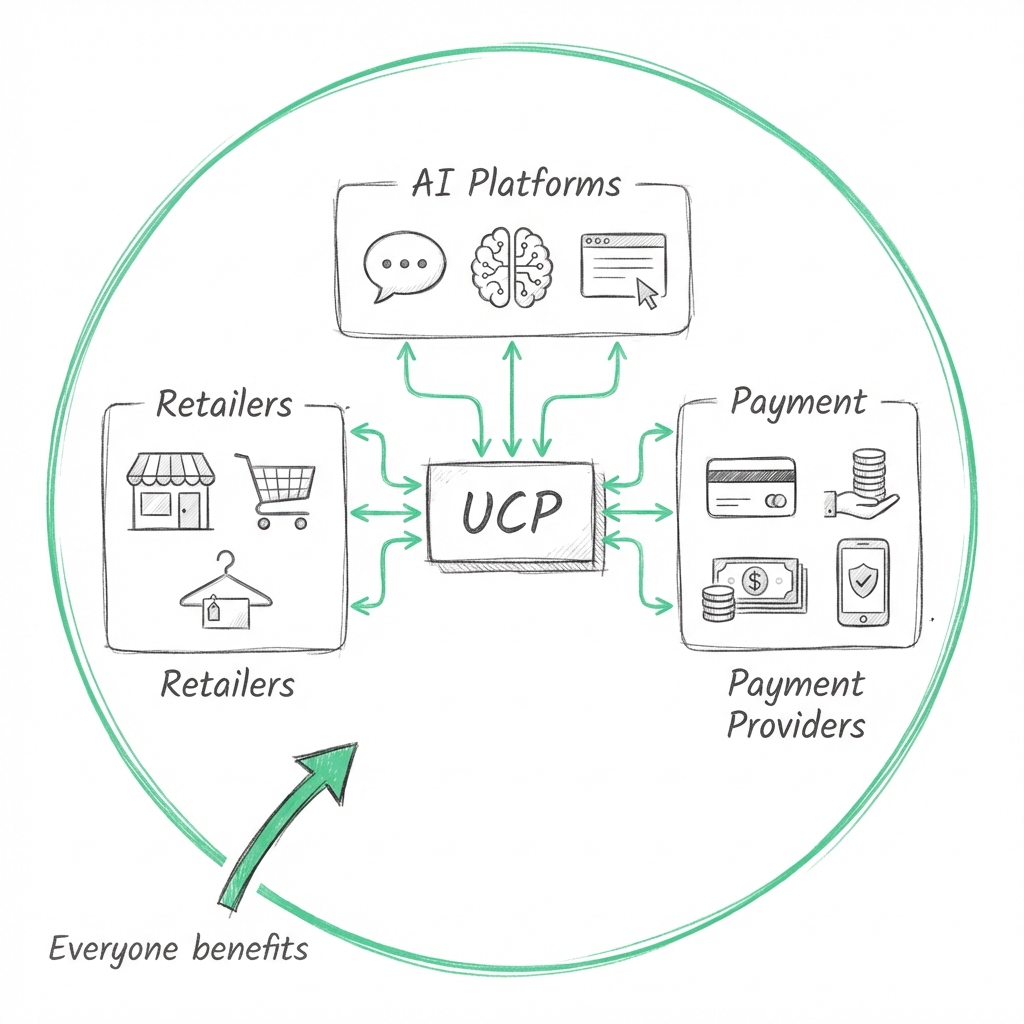
The Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) is a standardized technical specification that enables AI agents to interact with merchant stores across platforms.
How UCP Works
Traditional e-commerce requires customers (or AI) to interact with each store’s unique interface. UCP provides a common language:
- A customer makes a request to their AI assistant
- The AI agent queries merchants through UCP
- Merchants respond with structured product data
- The agent compares options and presents recommendations
- Upon approval, the agent completes checkout through UCP
- Payment processing occurs through integrated providers
What This Means for Merchants
Discovery: Your products become visible to AI shoppers, not just human browsers. Someone who never visits your website might purchase through their AI assistant.
Data quality becomes critical: AI agents rely on structured product information. Accurate descriptions, specifications, and availability data determine whether agents recommend your products.
New competitive dynamics: AI agents optimize for stated criteria (price, features, reviews, availability). Traditional advantages like brand awareness may matter less if the AI makes the selection.
For Shopify merchants, UCP is already integrated. Your products are discoverable to AI agents by default. However, the quality of your product data affects how well agents understand and recommend your offerings.
Preparing Your Shopify Store
Phase 0: Data Foundation
Agentic systems depend on data quality. Before implementing AI features:
- Audit product information: Ensure titles, descriptions, and specifications are accurate and complete
- Verify inventory sync: Stock levels should reflect reality across all channels
- Structure customer data: Clean, organized customer information improves personalization
- Review analytics setup: Accurate data collection enables better AI decisions
Most implementation issues trace back to data problems. This step isn’t optional.
Phase 1: Learn with Sidekick
Use Shopify’s built-in AI for low-risk tasks:
- Generate draft product descriptions
- Analyze sales data and identify trends
- Answer operational questions about your store
- Create basic email and campaign drafts
The goal is understanding how AI assistance works before giving it more autonomy.
Phase 2: Single Use Case
Select one area with:
- Good data quality
- Clear success metrics
- Low risk if something goes wrong
Inventory management often works well as a first use case. Run it for several months and measure results.
Phase 3: Measured Expansion
Based on Phase 2 results, add additional use cases. Each new area needs the same careful approach.
The objective isn’t maximum automation. It’s appropriate automation, with AI handling tasks that don’t require human judgment, allowing humans to focus on tasks that do.

Safety and Security Considerations
Safety requires attention to several areas.
AI Decision Errors
AI agents make mistakes. A pricing agent might set prices too aggressively. A content agent might produce off-brand messaging. A recommendation engine might suggest inappropriate products.
Mitigation: Implement guardrails limiting what agents can do without approval. Set boundaries on price changes. Review AI-generated content before publication. Monitor agent decisions and correct patterns.
Privacy and Data Use
Agentic systems analyze customer behavior extensively. Ensure compliance with privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA) and maintain transparent data practices. Customers should understand what data is collected and how it’s used.
Accountability Questions
If an AI agent makes a purchase that a customer disputes, who is responsible? This remains an evolving area. Current practice treats AI-initiated transactions like any other, with standard return and dispute processes applying.
Fraud Considerations
AI can be exploited for fraudulent purposes. Standard e-commerce fraud prevention measures apply, with additional monitoring for unusual AI-driven patterns.
Finding the Right Balance
Agentic commerce doesn’t mean automating everything. The goal is appropriate distribution of tasks between AI and humans.
AI handles effectively:
- Repetitive analysis across large datasets
- 24/7 monitoring and response
- High-volume routine transactions
- Pattern recognition and trend identification
Humans handle effectively:
- Strategic direction and goal-setting
- Creative decisions and brand voice
- Complex judgment with incomplete information
- Relationship management with key customers
Getting this balance wrong creates problems: overburdened staff if you automate too little, frustrated customers if you automate inappropriately.
Market Projections
Industry analysts project significant growth:
- McKinsey: Estimates the agentic commerce market could reach $3-5 trillion by 2030
- Morgan Stanley: Projects 20% of US online shopping could occur through AI agents by 2030
- Gartner: Predicts 40% of enterprise applications will include agentic AI capabilities by end of 2026
These projections involve uncertainty. The technology is new and adoption patterns are still forming. However, the direction is consistent across analyses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between AI agents and chatbots in e-commerce?
Chatbots respond to questions using scripts or keyword matching. They provide information but don’t take independent action. AI agents act autonomously: they trigger workflows, make decisions, execute transactions, and learn from results. A chatbot tells you your order shipped. An AI agent notices a delay, contacts you proactively, offers compensation, and flags the issue internally.
Do I need to be a large store to use agentic commerce?
No. Shopify’s built-in tools work at any scale. Sidekick is available to all Shopify merchants. UCP support is automatic. The difference is scope: smaller stores should start with basic AI features, while larger stores might implement custom agent workflows.
What is UCP and why does it matter?
The Universal Commerce Protocol is a standard that lets AI assistants interact with any participating merchant. It means your products can be discovered and purchased by AI shopping on behalf of customers. For Shopify merchants, UCP is built in. The main action item is ensuring your product data is complete and accurate.
How much does agentic commerce cost?
Costs vary by approach. Shopify Sidekick is included in standard plans. Third-party AI services typically range from $200-500/month for mid-size stores. Custom implementations cost more. The key calculation is whether efficiency gains exceed tool costs.
Will AI agents replace human staff?
Some tasks will shift from humans to AI. But new tasks emerge: overseeing AI decisions, handling exceptions, training systems. The composition of work changes more than the total amount. Stores that implement agentic features typically redeploy staff to higher-value activities rather than reducing headcount.



